[NestJs][typeorm] 기본적인 관계형 database를 만들어 보자
목차
자주 사용되는 TypreOrm 컬럼들
import {
Column,
CreateDateColumn,
Entity,
Generated,
OneToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
UpdateDateColumn,
VersionColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { ProfileModel } from './profile.entity';
enum Role {
USER = 'user',
ADMIN = 'admin',
}
enum Card {
USER = 'user',
YEAR = 'year',
}
@Entity()
export class UserModel {
//절대적으로 겹치지 않는 칼럼 생성
//PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
//Primary Column() -> 모든 테이블에서 기본적으로 존재해야 한다.
//테이블 안에서 각각의 Row를 구분 할 수 있는 칼럼이다.
//@PrimaryGeneratedColumn('uuid')
//PrimaryGeneratedColumn() -> 순서대로 위로 올라간다.
//
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
email: string;
@Column({
//데이터베이스에서 인지하는 칼럼 타입
default: 'default',
type: 'varchar',
//db칼럼 이름
name: 'title',
//null 가능 여부
nullable: false,
length: 10,
//true면 처음저장할 때만 값 지정 가능
//이후에는 값 변경 불가능
update: false,
//get 요청을 했을 때 거를 수 있음
//ex) 회원 가입 이메일
unique: false,
})
title: string;
@Column({
type: 'enum',
enum: Role,
default: Role.USER,
})
role: Role;
// 데이터 생성 일자
// 데이터가 생성되는 날짜와 시간이 자동으로 찍힘
@CreateDateColumn()
createAt: Date;
// 데이터 업데이트
//데이터가 업데이트되는 날짜와 시간이 자동으로 찍힘
@UpdateDateColumn()
updateAt: Date;
//데이터가 업데이트 될때마다 1씩 올라간다.
//처음 생성되면 값은 1이다.
@VersionColumn()
version: number;
//증가하는 숫자 생성 겹침 존재 가능
@Column()
@Generated('increment')
additionalId: number;
@Column()
@Generated('uuid')
additionalIdStr: string;
}
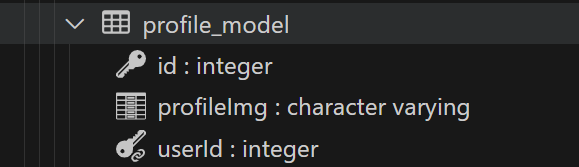
one-to-one relationship 만들기
profile 모델을 user 모델에 연결하기
UserModel entity
import {
Column,
Entity,
JoinColumn,
OneToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { UserModel } from './user.entity';
@Entity()
export class ProfileModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@OneToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.profile)
@JoinColumn()
user: UserModel;
@Column()
profileImg: string;
}
이때 @joinColum()은 외래키를 통해 관계의 주도권을 결정한다.
따라서 profileModel에 @JoinColumn을 썻기 때문에 UserModel이 주도권을 갖는다.
import {
Column,
CreateDateColumn,
Entity,
Generated,
OneToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
UpdateDateColumn,
VersionColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { ProfileModel } from './profile.entity';
@Entity()
export class UserModel {
.
.
.
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user)
profile: ProfileModel;
}
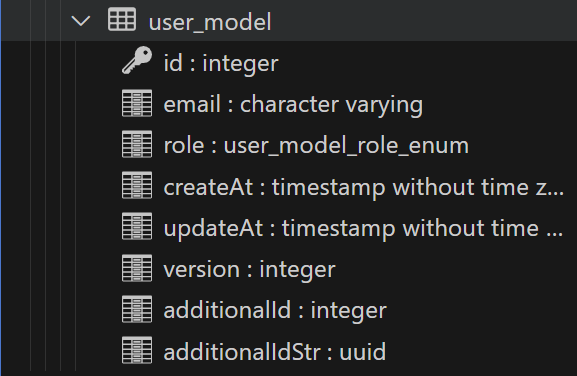
one-to-many relationship 만들기
PostModel entity
import {
Column,
Entity,
ManyToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { UserModel } from './user.entity';
@Entity()
export class PostModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.posts)
author: UserModel;
@Column()
title: string;
}
이때 @JoinColumn은 쓰지 않아도 된다.
자동으로 oneToMany를 가진 쪽이 주도권을 갖는다.
import {
Column,
CreateDateColumn,
Entity,
Generated,
OneToMany,
OneToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
UpdateDateColumn,
VersionColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { ProfileModel } from './profile.entity';
import { PostModel } from './post.entity';
@Entity()
export class UserModel {
.
.
.
@OneToMany(() => PostModel, (post) => post.author)
posts: PostModel[];
}

many-to-many relationship 만들기
many to many는 이해가 잘 안가서 정리하면 다음과 같다.
두 개의 entity를 참조하는 집합. 즉 테이블 두 개의 관계를 참조하는 또 하나의 테이블이 있는 상황이다.
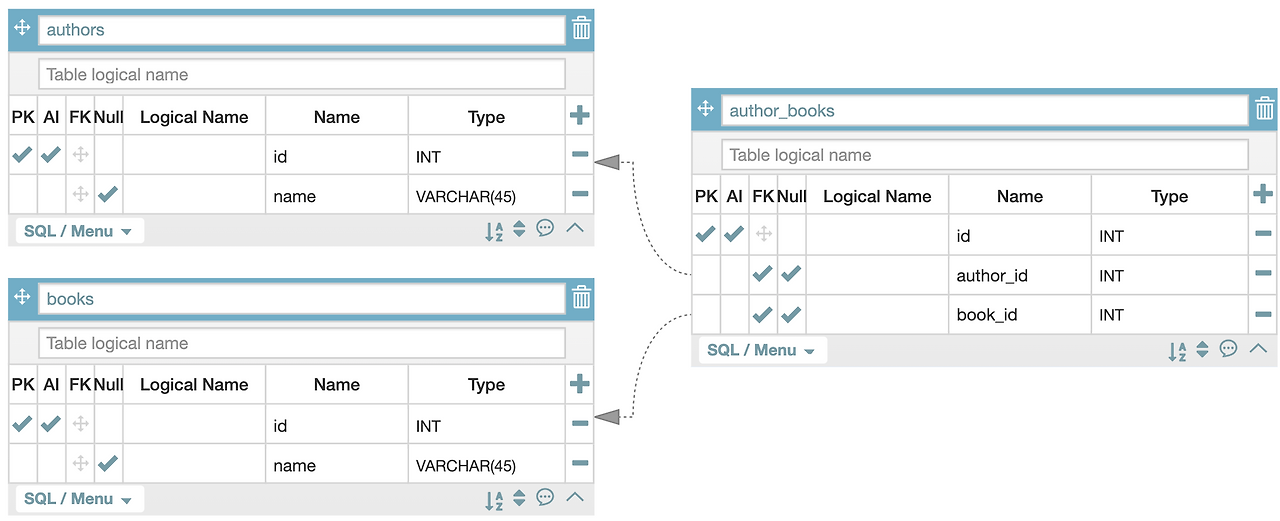
보통 게시물과 태그의 관계에서 이 관계가 쓰인다.
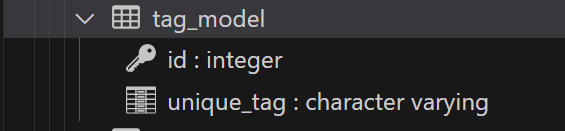
TagModel entity
import { Column, Entity, ManyToMany, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
import { PostModel } from './post.entity';
@Entity()
export class TagModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToMany(() => PostModel, (post) => post.tags)
posts: PostModel[];
//태그는 고유하므로 unique: true
@Column({
name: 'unique_tag',
unique: true,
})
name: string;
}
PostModel entity
한쪽에 joinTable을 통해 연결해 주어야 한다.
import {
Column,
Entity,
JoinTable,
ManyToMany,
ManyToOne,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { UserModel } from './user.entity';
import { TagModel } from './tag.entity';
@Entity()
export class PostModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.posts)
author: UserModel;
@ManyToMany(() => TagModel, (tag) => tag.posts)
@JoinTable()
tags: TagModel[];
@Column()
title: string;
}
다음과 같이 양방향 레퍼런스가 가능해진다.
app.controller.ts(서비스 로직 분리 x)
@Post('users/tags')
async cratePostsTags() {
const post1 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'NestJs',
});
const post2 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'NextJs',
});
const tag1 = await this.tagRepository.save({
name: 'javascript',
posts: [post1, post2],
});
const tag2 = await this.tagRepository.save({
name: 'typescript',
posts: [post2],
});
const post3 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'NodeJs',
tags: [tag1, tag2],
});
return true;
}
@Get('posts')
getPosts() {
return this.postRepository.find({
relations: {
tags: true,
},
});
}
@Get('tags')
getTags() {
return this.tagRepository.find({
relations: {
posts: true,
},
});
}

그외 관계형 옵션
eager: true
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user, {
eager: true,
})
profile: ProfileModel;
user.entity 에서 eager true옵션을 써주게 되면 relations로 get 옵션에 설정해 줄 필요가 없다.
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return this.userRepository.find({
relations: { //user와의 관계형 db가져옴
profile: true,
posts: true,
},
});
}
cascade:true
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user, {
cascade: true,
})
profile: ProfileModel;
이런식으로 한번에 저장할 수 있게 만들어 준다.
@Post('users/profile')
async createUserAndProfile() {
const user = await this.userRepository.save({
email: 'sins051301@naver.com',
profile:{
profileImg: 'asg.jpg'
}
});
// const profile = await this.profileRepository.save({
// profileImg: 'asd.jpg',
// user,
// });
return user;
}
nullable: false
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user, {
nallable: false,
})
profile: ProfileModel;기본 값은 true로 false로 설정하게 되면 null이 들어가면 500 에러가 발생하게 된다.
onDelete
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user, {
//관계가 삭제되었을 때
//no action-> 아무것도 안함
//cascade -> 참조하는 row도 같이 삭제
//set null -> 참조하는 row에서 참조 id를 null로 변경
//set default -> 기본 세팅으로 설정 (테이블의 기본 세팅)
//restrict -> 참조하고 있는 row가 있는 경우 참조당하는 row 삭제 불가
onDelete: 'CASCADE',
})
주의
OneToOne 관계는 @JoinColumn의 위치에 따라 어떤 테이블에서 Foreign Key를 레퍼런스 하고 있을지 결정하게 되는데
이것에 따라 삭제의 전파 여부가 다르게 결정된다.
또한 JoinColumn을 한 곳에 cascade를 써주어야 한다.
get 관련 필터 옵션
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return this.userRepository.find({
//어떤 프로퍼티를 선택할지
//기본은 모든 프로퍼티를 가져온다.
//만약에 select를 정의하지 않으면
//select를 정의하면 정의한 프로퍼티를 가져온다.
select: {},
//필터링할 조건을 입력하게 된다.
where: [
{
version: 2,
},
{
id: 7,
},
],
//ASC -> 오름차
//DESC -> 내림차
order: {
id: 'ASC',
},
//처음 몇개를 제외할지
skip: 2,
//첫번째부터 몇개를 가져올지
take: 0,
});
}
그 외 자주 사용되는 typeorm method 정리
preload
//preload
//입력된 값을 기반으로 데이터베이스에 있는 데이터를 불러오고
//추가 입력된 값으로 데이터베이스에서 가져온 값을 대체함
// 저장하지는 않음
const user3 = await this.userRepository.preload({
id: 101,
email: 'coding@naver.com',
});
decrement / increment
// 값을 감소시킴
await this.userRepository.decrement(
{
id: 8,
},
'count',
2,
);
//값을 증가시킴
await this.userRepository.increment(
{
id: 8,
},
'count',
2,
);
count
//갯수 카운팅하기
const count = await this.userRepository.count({
where: {
email: ILike('%0%'),
},
});
sum
//sum
const sum = await this.userRepository.sum('count', {
email: ILike('%@%'),
});
average
//average
const average = await this.userRepository.average('count', {
id: LessThan(4),
});
min / max
const min = await this.userRepository.minimum('count', {
id: LessThan(10),
});
const max = await this.userRepository.maximum('count', {
id: LessThan(10),
});
findAndCount
//페이지네이션할 때 유용 take안했을 때 count도 가져옴
const userAndCount = await this.userRepository.findAndCount({
take: 3,
});
강의출처
[코드팩토리] [초급] NestJS REST API 백엔드 완전 정복 마스터 클래스 - NestJS Core 강의 | 코드팩토리 -
코드팩토리 | 자바스크립트, 타입스크립트 다음은 백엔드 개발! NestJS를 이용한 REST API 백엔드 개발, Socket IO 개발 및 배포를 할 수 있게 됩니다., 백엔드가 처음이어도 누구나 OK! 트렌디한 NestJS로
www.inflearn.com