목차
Interceptor란?
아래 life cycle를 통해 알 수 있듯이 interceptor는 request와 response에서 둘다 작동한다.
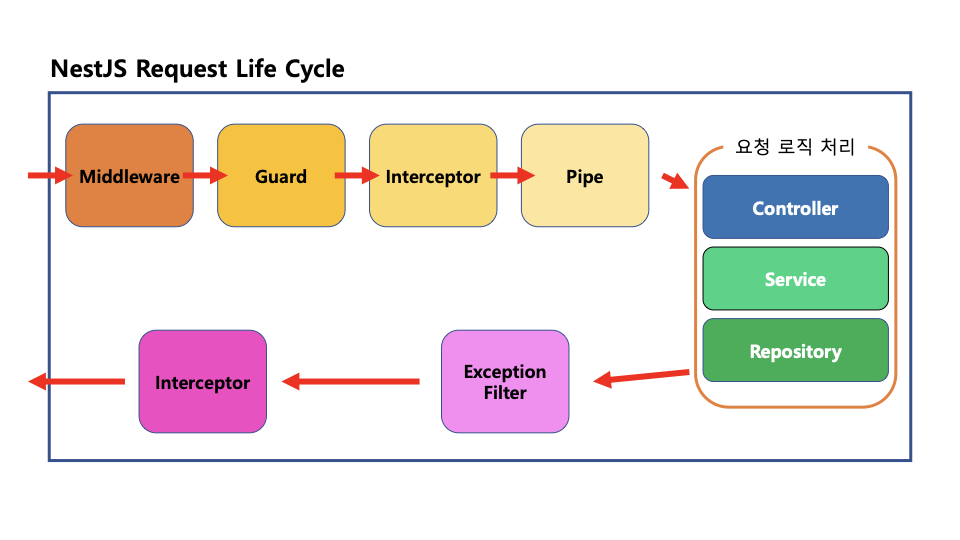
공식 문서에서는 다음과 같이 설명한다.
인터셉터(Interceptors)는 관점 지향 프로그래밍(AOP, Aspect-Oriented Programming) 기술에서 영감을 받은 다양한 기능을 제공한다. 이를 통해 다음과 같은 작업이 가능하다:
- 메서드 실행 전/후에 추가 로직을 바인딩할 수 있다.
- 함수가 반환하는 결과를 변환할 수 있다.
- 함수에서 발생한 예외를 변환할 수 있다.
- 기본 함수의 동작을 확장할 수 있다.
- 특정 조건(예: 캐싱 목적)에 따라 함수를 완전히 재정의할 수 있다.
interceptor를 다루게 되면 rxjs를 알아야 한다.
아래 잘 설명이 되어있으므로 참고 해보자
Rxjs 한번 배워보실래요?
나: "그래서 RxJs를 대체 할 만한게 있을까요?" > 크루: "솔직히 비동기나 시간을 다루는 데에는 Rxjs를 대체 할 만한게 없긴 하죠. 진짜 좋다고 생각해요. ... 배우기 어려워서 그렇지. 웬만한 개발자
velog.io
tab, pipe, map 등 주요 메서드만 알아도 사용하는데 크게 문제는 안될 것 같다.
시간 측정용 로그 interceptor 만들어 보기
log.interceptor.ts
import {
CallHandler,
ExecutionContext,
Injectable,
NestInterceptor,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { map, Observable, tap } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class LogInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(
context: ExecutionContext,
next: CallHandler<any>,
): Observable<any> {
/**
* 요청이 들어올 때 REQ 요청이 들어온 타임스탬프를 찍는다.
* [REQ] {요청 path} {요청 시간}
*
* 요청이 끝날 때 (응답이 나갈때) 다시 타임스탬프를 찍는다.
* [RES] {요청 path} {응답 시간} {얼마나 걸렸는지 ms}
*/
const req = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
const path = req.originalUrl;
const now = new Date();
console.log(`[REQ] ${path} ${now.toLocaleString('kr')}`);
// return next.handle()을 실행하는 순간
// 라우트의 로직이 전부 실행되고 응답이 반환된다.
// observable로
return next.handle().pipe(
// tap((observable) => console.log(observable)),
// map((observable) => {
// return {
// message: '응답이 변경 됐습니다.',
// response: observable,
// };
// }),
// tap((observable) => console.log(observable)),
tap((observable) =>
console.log(
`[RES] ${path} ${new Date().toLocaleString('kr')} ${new Date().getMilliseconds() - now.getMilliseconds()}ms `,
),
),
);
}
}
posts.controller.ts
@Get()
@UseInterceptors(LogInterceptor)
getPosts(@Query() query: paginatePostDto) {
return this.postsService.paginationPosts(query);
// return this.postsService.getAllPosts();
}
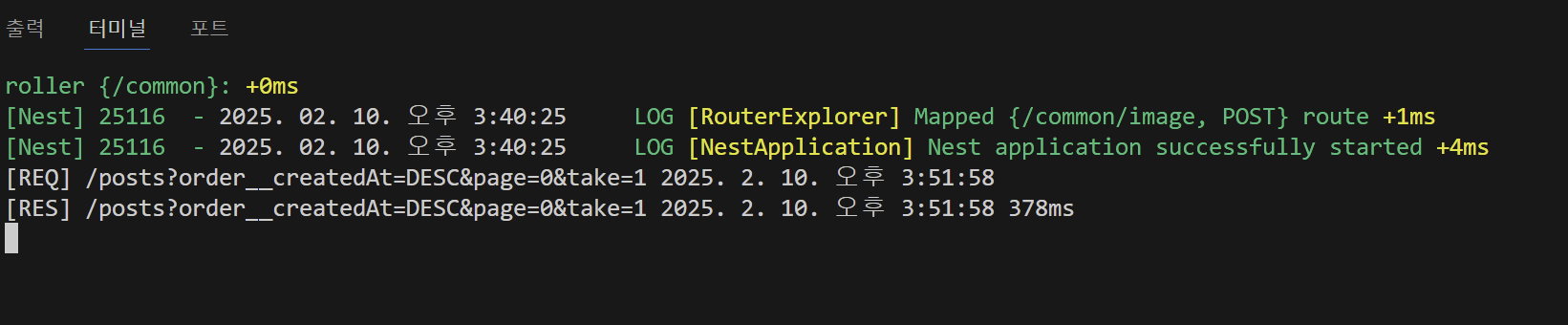
아래와 같이 잘 나오는 것을 볼 수 있다.
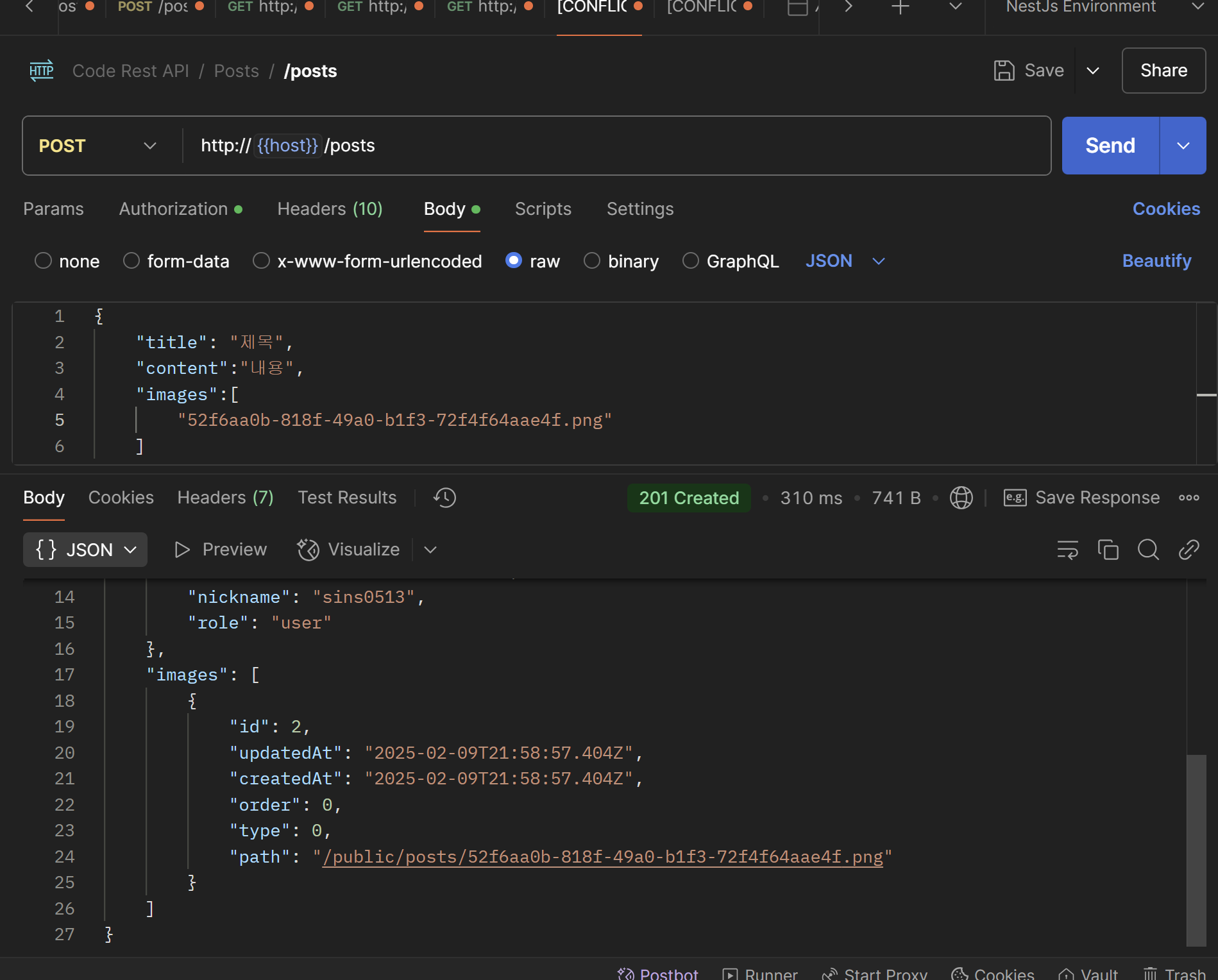
transaction용 interceptor 만들어 보기
이전에 만들었던 트랜잭션용 코드를 보자
request와 response로 나누어 충분히 interceptor를 만드는 것이 가능해 보인다.
@Post()
@UseGuards(AccessTokenGuard)
async postPosts(@User('id') userId: number, @Body() body: CreatePostDto) {
//오류 생기면 롤백되야 함
//트랜잭션과 관련된 모든 쿼리를 담당할
//쿼리 러너를 생성한다.
const qr = this.dataSource.createQueryRunner();
//쿼리 러너에 연결한다.
await qr.connect();
//쿼리 러너에서 트랜잭션을 시작함
//이 시점부터 같은 쿼리 러너를 사용하면
// 트랜잭션 안에서 데이터베이스 액션을 실행 할 수 있다.
await qr.startTransaction();
//로직 실행
try {
const post = await this.postsService.createPost(userId, body, qr);
//throw new InternalServerErrorException("트랜잭션 에러 확인용")
for (let i = 0; i < body.images.length; i++) {
await this.postsImageService.createPostImage(
{
post,
path: body.images[i],
order: i,
type: ImageModelType.POST_IMAGE,
},
qr,
);
}
await qr.commitTransaction();
await qr.release();
return this.postsService.getPostById(post.id);
} catch (e) {
//어떤 에러든 에러가 던져지면
//트랜잭션을 종료하고 원래 상태로 되돌린다.
await qr.rollbackTransaction();
await qr.release();
throw new InternalServerErrorException("포스트 에러 발생")
}
}
transaction.interceptor.ts
import {
CallHandler,
ExecutionContext,
Injectable,
InternalServerErrorException,
NestInterceptor,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { catchError, map, Observable, tap } from 'rxjs';
import { DataSource } from 'typeorm';
@Injectable()
export class TransactionInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
constructor(private readonly dataSource: DataSource) {}
async intercept(
context: ExecutionContext,
next: CallHandler<any>,
): Promise<Observable<any>> {
const req = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
//트랜잭션과 관련된 모든 쿼리를 담당할
//쿼리 러너를 생성한다.
const qr = this.dataSource.createQueryRunner();
//쿼리 러너에 연결한다.
await qr.connect();
//쿼리 러너에서 트랜잭션을 시작함
//이 시점부터 같은 쿼리 러너를 사용하면
// 트랜잭션 안에서 데이터베이스 액션을 실행 할 수 있다.
await qr.startTransaction();
req.queryRunner = qr;
return next.handle().pipe(
catchError(async (e) => {
await qr.rollbackTransaction();
await qr.release();
throw new InternalServerErrorException(e.message);
}),
tap(async () => {
await qr.commitTransaction();
await qr.release();
}),
);
}
}
우리는 qr을 가져다 써야하므로 데코레이터를 통해 가져와 보자
데코레이터를 통해 queryRunner 가져오기
query-runner.decorator.ts
import {
createParamDecorator,
ExecutionContext,
InternalServerErrorException,
} from '@nestjs/common';
export const QueryRunner = createParamDecorator(
(_, context: ExecutionContext) => {
const req = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
if (!req.queryRunner) {
throw new InternalServerErrorException(
'QueryRunner Decorator를 사용하려면 TransactionInterceptor를 사용해야 합니다',
);
}
return req.queryRunner;
},
);
아래와 같이 로직이 잘 정돈 된것을 볼 수 있다.
@Post()
@UseGuards(AccessTokenGuard)
@UseInterceptors(TransactionInterceptor)
async postPosts(
@User('id') userId: number,
@Body() body: CreatePostDto,
@QueryRunner() qr: Qr,
) {
//로직 실행
const post = await this.postsService.createPost(userId, body, qr);
//throw new InternalServerErrorException("트랜잭션 에러 확인용")
for (let i = 0; i < body.images.length; i++) {
await this.postsImageService.createPostImage(
{
post,
path: body.images[i],
order: i,
type: ImageModelType.POST_IMAGE,
},
qr,
);
}
return this.postsService.getPostById(post.id, qr);
}
강의출처
[코드팩토리] [초급] NestJS REST API 백엔드 완전 정복 마스터 클래스 - NestJS Core 강의 | 코드팩토리 -
코드팩토리 | , 백엔드가 처음이어도 누구나 OK! 트렌디한 NestJS로 서버 개발을 배워보세요. NestJS 프레임워크 마스터 클래스 : Part 1 Node.js 기반 백엔드 서버 프레임워크, NestJS의 라이프사이클에서
www.inflearn.com
'코딩 정보 > NestJs' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [NestJs] middleware를 구현해 보자 (0) | 2025.02.10 |
|---|---|
| [NestJs] Exception Filter를 구현해 보자 (0) | 2025.02.10 |
| [NestJs] 트랜잭션을 구현해 보자 (0) | 2025.02.08 |
| 이미지 업로드를 구현해 보자 (하) (2) | 2025.02.05 |
| [NestJs] 이미지 업로드를 구현 해보자 (0) | 2025.02.04 |